Decoding Body Language: Psychological Interpretations of Non-Verbal Cues

Communication extends far beyond spoken words. In fact, much of what we convey and perceive is communicated through non-verbal cues, such as body language, facial expressions, and gestures. Understanding and interpreting these signals can provide invaluable insights into a person’s thoughts, feelings, and intentions. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of body language and explore how psychological principles can help you decode non-verbal cues like a pro.
The Language of the Body
Body language is a universal form of communication that transcends cultural and linguistic barriers. From subtle facial expressions to unconscious gestures, our bodies constantly convey information about our inner thoughts and emotions. By learning to recognize and interpret these signals, you can gain deeper insights into interpersonal dynamics and enhance your communication skills.
1. Facial Expressions: The face is a rich canvas of emotions, with countless microexpressions conveying subtle nuances of feeling. For example, a furrowed brow may indicate confusion or concern, while a genuine smile can signal happiness or amusement. By paying attention to facial expressions, you can gain valuable clues about a person’s emotional state and authenticity.

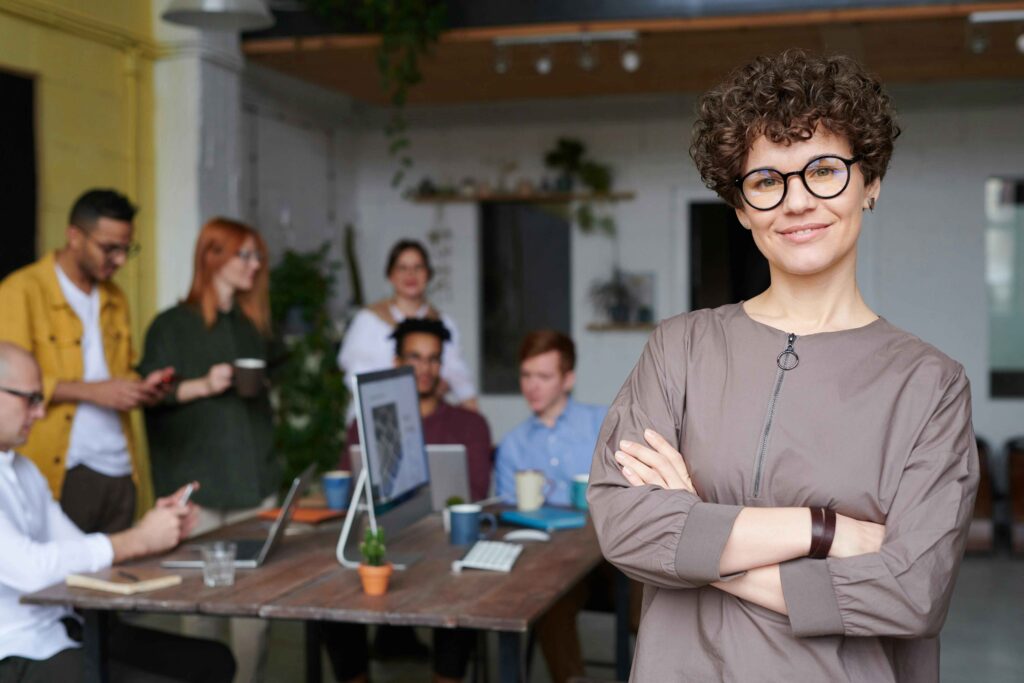
2. Gestures and Posture: Gestures and posture also play a significant role in communication, reflecting attitudes, intentions, and levels of confidence. For instance, crossed arms may indicate defensiveness or discomfort, while open and expansive gestures can convey confidence and openness. Similarly, upright posture often signifies attentiveness and engagement, while slouched posture may suggest disinterest or fatigue.
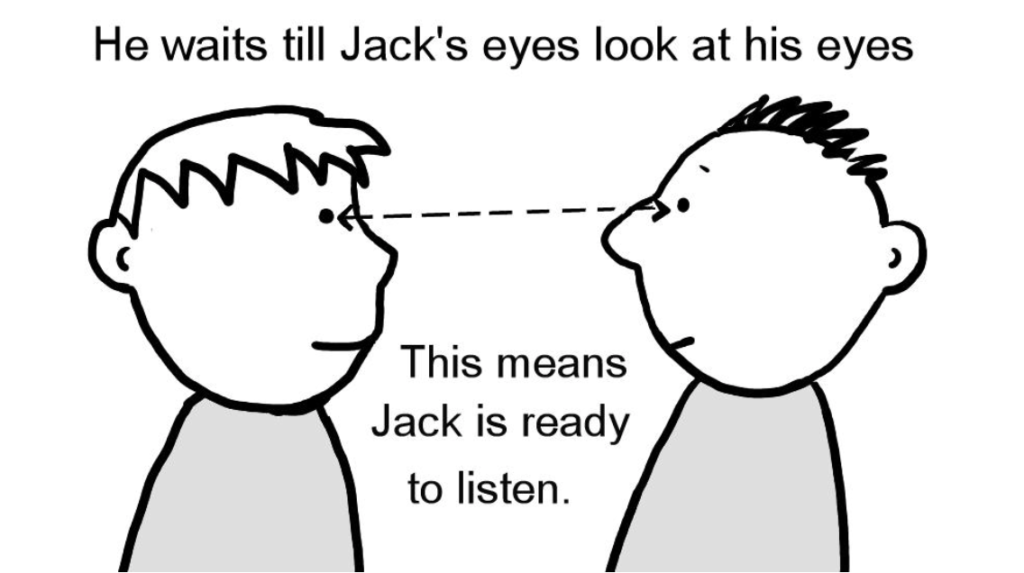
3. Eye Contact: The eyes are often described as the windows to the soul, revealing a wealth of information about a person’s thoughts and feelings. Sustained eye contact can convey sincerity, confidence, and connection, while averted gaze may signal discomfort, shyness, or dishonesty. Understanding the nuances of eye contact can help you gauge the level of rapport and trust in a social interaction.
4. Touch: Touch is a powerful form of non-verbal communication, capable of conveying warmth, support, and intimacy. A reassuring pat on the back, a firm handshake, or a gentle embrace can communicate empathy, solidarity, and affection. However, it’s essential to respect personal boundaries and cultural norms when interpreting and initiating physical contact.
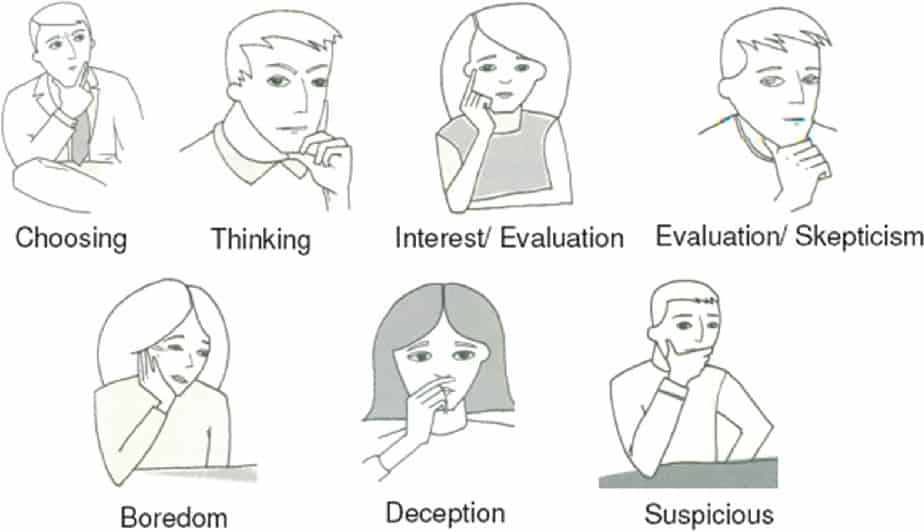
The Psychology Behind Body Language
The interpretation of body language is deeply rooted in psychological principles and theories. Psychologists have long studied the relationship between non-verbal cues and underlying thoughts, emotions, and motivations, shedding light on the intricate dance of communication unfolding beneath the surface.
1. Emotional Expression: The facial feedback hypothesis suggests that our facial expressions can influence our emotional state. By observing the expressions of others, we can gain insights into their emotional experiences and empathize with their feelings. For example, mirroring someone’s smile can evoke a sense of camaraderie and connection.

2. Social Influence: Body language plays a crucial role in social influence and persuasion. According to research on the psychology of persuasion, mirroring the body language of others can establish rapport and increase compliance. By subtly matching the posture, gestures, and vocal tone of your conversation partner, you can create a sense of affinity and cooperation.
3. Deception Detection: Detecting deception is a complex process that involves analyzing verbal and non-verbal cues for inconsistencies and discrepancies. While there is no foolproof method for detecting lies, research suggests that certain non-verbal behaviors, such as averted gaze, fidgeting, or vocal hesitations, may indicate deception. However, it’s essential to consider individual differences and context when interpreting these cues.
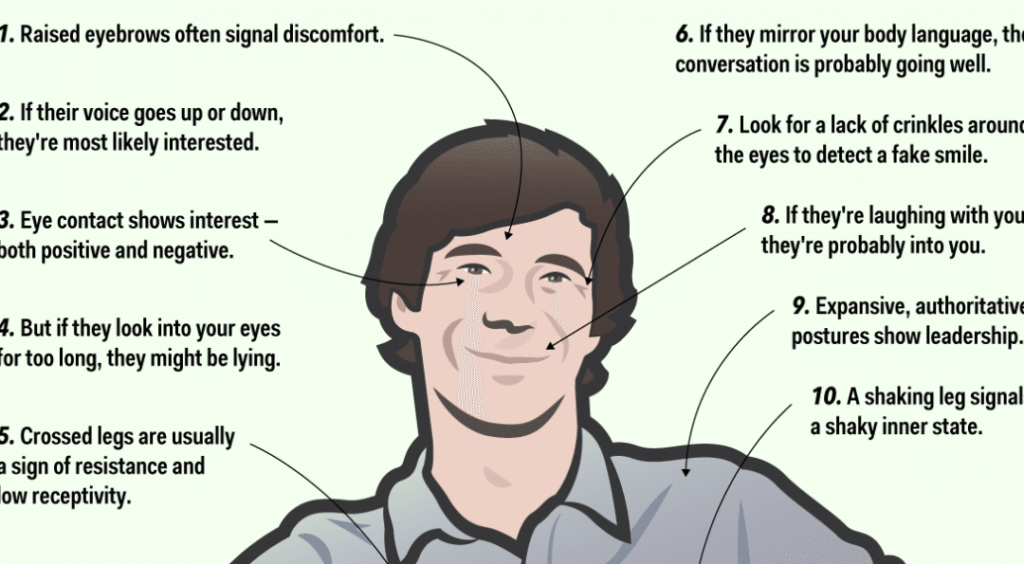
Practical Tips for Decoding Body Language
Now that we’ve explored the psychology behind body language, let’s discuss some practical tips for honing your skills in decoding non-verbal cues:
1. Observe Actively: Pay close attention to the body language of others during conversations, meetings, and social interactions. Notice facial expressions, gestures, and posture, and consider how they align with verbal communication.
2. Consider Context: Context is key when interpreting body language. Take into account the situational factors, cultural norms, and individual differences that may influence non-verbal behaviour.
3. Be Mindful of Your Own Body Language: Awareness of your own non-verbal cues can enhance your effectiveness as a communicator. Practice open and confident body language, maintain eye contact, and use gestures to reinforce your verbal message.

4. Seek Feedback: Solicit feedback from trusted friends, colleagues, or mentors on your ability to interpret and convey non-verbal cues. Constructive feedback can help you refine your skills and deepen your understanding of body language.
Conclusion
Decoding body language is both an art and a science, requiring keen observation, empathy, and an understanding of psychological principles. By learning to recognize and interpret non-verbal cues, you can enhance your communication skills, build rapport with others, and navigate social interactions with confidence and insight. Whether you’re negotiating a business deal, interviewing for a job, or simply engaging in everyday conversations, mastering the language of the body can open doors to deeper connections and more meaningful relationships. So, sharpen your observation skills, tune into the subtle cues of non-verbal communication, and unlock the secrets hidden beneath the surface.





Responses