The Psychology behind Loneliness: Understanding the Silent Struggle

Loneliness is a universal human experience, but its psychological underpinnings are often misunderstood or overlooked. It’s a feeling that transcends age, gender, and social status, affecting millions of people worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the psychology behind loneliness, exploring its causes and consequences, and offering insights on how to combat it.
Loneliness: The Universal Human Experience
Loneliness is not merely a physical state of being alone; it’s a deep emotional experience. It can be felt in a crowded room or while surrounded by friends and family. This is because loneliness is more about the quality of our relationships and our perception of social support rather than just the quantity of people around us.
What Causes Loneliness?
1. Social Isolation
Loneliness often stems from social isolation, where people lack meaningful connections and interactions. Whether due to physical distance, a busy lifestyle, or personal circumstances, isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness.
2. Quality of our Relationship
Even if you have many acquaintances, if your relationships lack depth and emotional connection, you may still experience loneliness. It’s the quality of interactions that matters most.
3. Life Transitions
Major life changes, such as moving to a new city, losing a loved one, or going through a breakup, can trigger loneliness. These transitions disrupt familiar social networks and support systems.
4. Technology and Social Media
Paradoxically, the digital age has given rise to “social loneliness.” Spending too much time on social media can lead to feelings of disconnection, as it often fosters superficial interactions and social comparison.
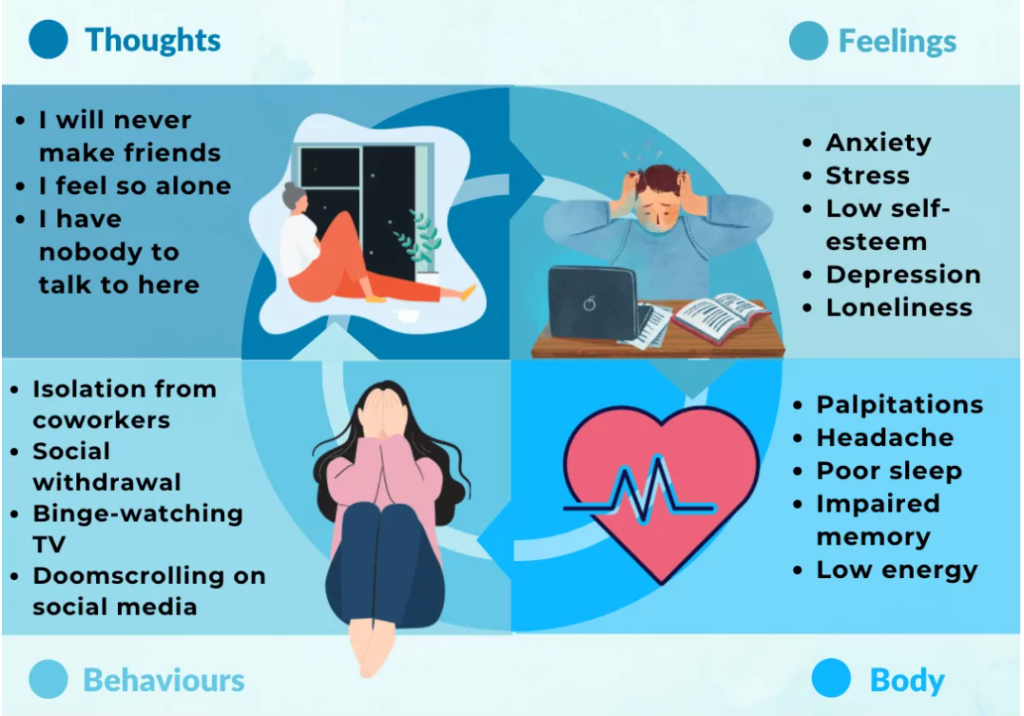
The Vicious Cycle of Loneliness

Loneliness can lead to a vicious cycle of negative emotions and behaviors. When people feel lonely, they may experience increased stress, anxiety, and even depression. This, in turn, can lead to self-imposed social withdrawal, exacerbating feelings of isolation.
The Cognitive Aspect
Psychology plays a significant role in loneliness. Our thoughts and beliefs can contribute to the feeling of being alone. For instance, people who hold negative self-perceptions or have a constant fear of rejection may find it challenging to form and maintain social connections. Cognitive biases, like assuming others don’t like you, can intensify feelings of loneliness.
The Consequences of Loneliness
Loneliness is not just an unpleasant feeling; it can have profound implications for mental and physical health. Research has shown that chronic loneliness is associated with increased stress, depression, anxiety, and a weakened immune system. Furthermore, lonely individuals may have a shorter life expectancy and an increased risk of developing chronic health conditions, such as heart disease.
Overcoming Loneliness
Understanding the psychology of loneliness is the first step in addressing this pervasive issue. Here are some strategies to combat loneliness:
1. Foster Meaningful Connections: Seek out and nurture relationships that offer emotional depth and support. Join clubs, groups, or engage in activities that align with your interests and values.
2. Digital Detox: While technology can help connect people, it can also exacerbate feelings of loneliness. Consider limiting your screen time and having real, face-to-face interactions.
3. Challenge Negative Thoughts: If you find yourself trapped in a cycle of self-doubt and fear of rejection, consider cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to reframe your thought patterns.
4. Self-Compassion: Practicing self-compassion can improve self-esteem and make it easier to form connections with others.
5. Professional Help: If loneliness is causing severe distress or affecting your daily life, don’t hesitate to seek the assistance of a mental health professional.
Conclusion
Loneliness is a complex emotion rooted in our psychological and emotional well-being. It’s a universal human experience, and understanding its causes and consequences is essential for combating this silent epidemic. By fostering meaningful relationships, challenging negative thoughts, and seeking help when needed, we can all work towards overcoming loneliness and leading happier, healthier lives.





Dr Pradeep ji really it’s too nice & very helpful articles for mental health.
Thanks 👍
Definitely believe that which you stated. I definitely get
irked while people think about worries that they plainly don’t know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as
defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks